The LNC’s Analysis of a Failure to Rescue Case
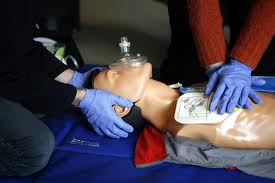 Failure to rescue is a devastating clinical event and a devastating accusation against a nurse. A nurse walks into a patient’s room and recognizes the patient is not breathing and has no pulse. The nurse starts CPR and alerts the cardiac resuscitation team. After trying medications and shock, the team is unable to restore the patient’s heart beat. They sadly walk away.
Failure to rescue is a devastating clinical event and a devastating accusation against a nurse. A nurse walks into a patient’s room and recognizes the patient is not breathing and has no pulse. The nurse starts CPR and alerts the cardiac resuscitation team. After trying medications and shock, the team is unable to restore the patient’s heart beat. They sadly walk away.
Legal nurse consultant’s analysis of failure to rescue case
Could this death have been prevented? Were there early warning signs that were overlooked? Your attorney client calls you about a case involving a man who went into respiratory distress on a medical surgical unit. She is requesting your analysis of the case.
Many failure to rescue cases are preventable with early intervention. Several medical studies have shown that there are early warning signs that help identify patients whose conditions are deteriorating – minutes to hours before a serious adverse event occurs. In many cases, there is enough time to identify patients who are at risk for an adverse event, and to intervene.
There are observable signs of deterioration that develop within 6-8 hours before a cardiac arrest. Sixty to ninety five percent of cardiac arrests are potentially avoidable depending on where the patient is receiving care. Up to 80 percent of people who have a cardiac arrest do not survive.
Early warning signs of clinical deterioration
This is an easy way to remember the early warning signs. Use the ABCCCs:
Airway:
- The patient may have a blockage in the airway.
- The patient’s breathing may be noisy or labored.
- There may be a problem with a tracheostomy tube.
Breathing:
- Any difficulty with breathing is a warning sign.
- The patient may be breathing less than 8 breaths per minute.
- The patient may be breathing more than 25 breaths per minute.
- The patient’s oxygen saturation may be 90 or less, despite receiving oxygen.
Circulation:
The first C stands for circulation. These are early warning signs:
- A pulse of 40 beats per minute or less
- A pulse of 120 beats per minute or more
- Low blood pressure with the systolic value less than 90
- Urine output of less than 50 cc over 4 hours
Conscious state:
The second C stands for conscious state:
- There is a sudden change in conscious state or the patient cannot be awakened.
Concern:
The last C stands for concern:
- This refers to the situation in which a healthcare provider having intuition or a gut feeling that there is something wrong with the patient. This is sometimes referred to as “the staff are worried about the patient”.
Medical Causes of Early Warning Signs of Clinical Deterioration
There are a number of medical conditions which can cause early warning signs of a change in the patient’s condition. These include
- Acute respiratory failure
- Acute cardiac failure
- Acute changes in consciousness
- Hypotension
- Arrhythmias
- Pulmonary edema
- Sepsis
Liability Theories in Failure to Rescue
Consider these possible liability theories.
1. Failure to recognize the man’s deteriorating condition
The healthcare provider might have
- lacked experience or skills
- been unwilling to request help from a more experienced or higher credentialed physician
- put too much emphasis on the diagnostic studies instead of looking at the patient
- not have understood or conveyed the urgency of the situation
- lacked knowledge
- pursued the wrong diagnosis
2. Barriers to escalating the attention the man needed
The healthcare provider may have
- not understood how to get help for the patient
- not known when to request help
- not have senior healthcare providers available
- been fearful of being chastised
- hit resistance from a senior physician
A nine-day-old premature infant was diagnosed with a cardiac abnormality which required a cardiac catheterization. During the procedure the infant’s pulmonary valve membrane was perforated, and the bleeding was recognized and treated. Also during the cardiac catheterization, the infant’s femoral vein was cut in half, but this injury was not recognized. Within hours, the infant had an acute hemorrhage with changes in its vital signs consistent with bleeding. The staff urgently requested the neonatologist to order arterial blood gas testing, which the physician would not do. The physician also failed to order an assessment of the leg, monitoring and blood transfusions. Within five and a half hours the child died from the bleeding. The physician settled the case for $1,275,000.
Legal Nurse Consultant Assistance with Failure to Rescue Case
Your role as a legal nurse consultant helping an attorney with a failure to rescue case could encompass:
- Explaining how the healthcare system operates
- Describing the cascade of medical events
- Creating a timeline
- Suggesting items to obtain during discover
- Preparing questions for depositions
- Securing expert witnesses
- and more
In part 2, I discuss more about failure to rescue, the critical role of the rapid response team and how providers prevent these events.
Pat Iyer MSN RN LNCC assisted attorneys for 28 years as president of Med League, a company she sold in 2015. She is the past president of the American Association of Legal Nurse Consultants. She now coaches LNCs who want to skyrocket their skills. Discover more at www.LNCAcademy.com.

